But the real power of BI tools lies in the hands of the BI team. These are the people who run the BI software, make sense of the data, and pull out useful insights that can help shape important business decisions and boost business performance.
In this article, we’re going to give you a full rundown on how to set up a BI team. We’ll cover everything from laying down clear business goals to putting together a solid plan for managing your data. We’ll also look at the different roles in a BI team and how to effectively staff and scale your team.
Before you build your BI team
Before forming a Business Intelligence (BI) team, it’s important to have some things in place.
These elements is the foundation for the team’s operations, strategy, and integration within the business:
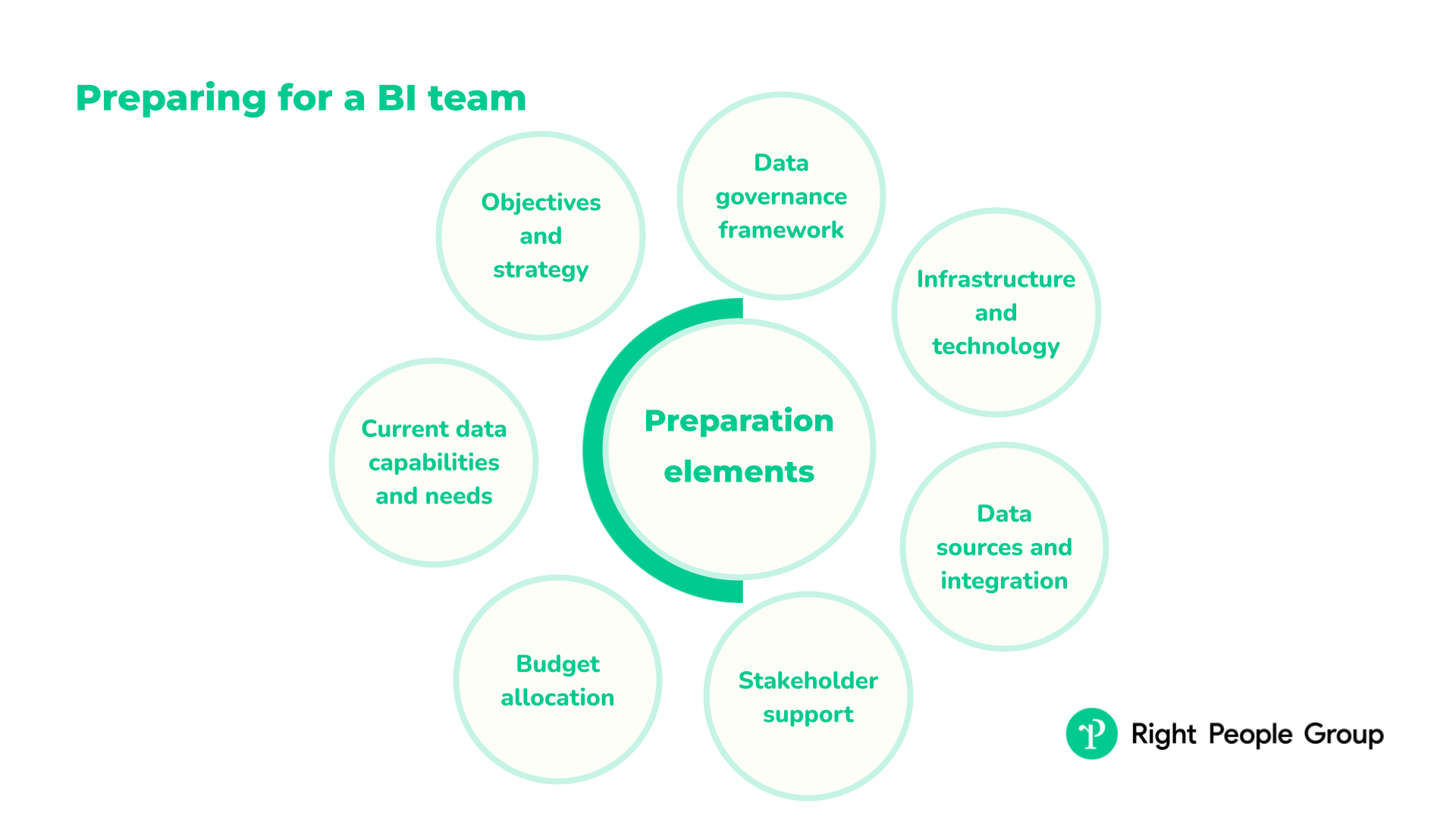
- Clear business objectives and strategy: You must have a clear understanding of your company’s strategic goals. This understanding will guide your BI initiatives and ensure that whatever your BI team does, it will help you achieve specific business outcomes. Without direction or focus on areas, they won’t be able to contribute anything worthwhile.
- Data governance framework: A data governance framework specifies policies and standards for data management, quality, security, and privacy. Have this framework ready before the BI team is in place so that they have rules and guidelines for handling data in a compliant and consistent way.
- Data infrastructure and technology: The BI team requires a strong data infrastructure to work effectively. This includes databases, data warehouses, and relevant hardware and software tools. Have the infrastructure in place so that the BI team has the necessary tools and systems to start their work immediately.
- Data sources and integration: The team needs access to relevant, high-quality data from various sources within and outside the organization. Pre-establishing these data sources and integration ensures that the BI team can immediately begin extracting insights.
- Stakeholder buy-in and support: Gaining support from top management and key stakeholders is crucial to getting the resources needed, ensuring everyone in the organization is on board, and helping the BI team work well with other departments.
- Budget allocation: A dedicated budget for BI initiatives includes funds for tools, technology, personnel, and training. Having a budget in place ensures that the BI team has the financial resources to operate effectively.
As a starting point, it’s advisable to consult with BI experts or conduct a market analysis to get a more precise estimate based on your organization’s specific needs.
- Understanding of current data capabilities and needs: Taking a close look at your organization’s current data capabilities and needs helps you define exactly what your BI team should be focusing on.
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses in your data infrastructure allows you to pinpoint where your organization can benefit the most from enhancing its data intelligence.
Core roles and responsibilities
Putting together a team that can skillfully analyze and make the most of data to drive business growth is no small feat. When it comes to building your Business Intelligence (BI) team, it’s essential to pick the right people with precision, define their roles clearly, and employ effective recruitment strategies.
In this section, we’ll focus on the core roles that a business intelligence team is made out of.
1. BI analyst
The BI Analyst is crucial in any BI team, serving as the bridge between raw data and strategic insights. These professionals excel in deciphering complex data sets, transforming them into understandable and actionable insights that drive decision-making.
Responsibilities:
- Data analysis: The primary task of a BI analyst is to analyze data. This involves discerning what insights are valuable for the business and understanding what the data is saying.
- Dashboard development: They are responsible for developing BI dashboards. These dashboards are crucial for providing accessible insights to various stakeholders across the organization.
- Report generation: Generating reports that inform business strategies is a key responsibility. These reports should present data and offer insights and recommendations based on that data.
- Business requirements translation: A significant part of their role involves understanding business requirements and translating them into data-driven solutions. Business analytics requires a deep understanding of both the business domain and the data landscape.
Qualifications and skills:
- Educational background: Business intelligence analysts are typically expected to have a Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science, Business, or a related field. This educational foundation provides them with the necessary theoretical understanding of data and business processes.
- Technical proficiency: They should be proficient in data analysis and data visualization, using tools like Tableau and Power BI. This skill set is essential for turning raw data into visually compelling and easy-to-understand reports.
- Analytical acumen: Strong analytical skills are non-negotiable. A business intelligence analyst must possess the ability to interpret complex data and identify trends, patterns, and anomalies.
Top tip: When recruiting a BI Analyst, look beyond technical skills. Consider candidates who demonstrate a keen understanding of business processes and possess the ability to think strategically about data.
2. Data architect
Data architects are key in shaping how an organization uses its data. They build and look after the data framework, which is essential for all Business Intelligence (BI) activities. Their role is to create a data system that’s efficient and fits the business’s long-term goals.
Responsibilities:
- Data warehouse design: One of their primary responsibilities is designing the data warehouse architecture. This involves creating a scalable and efficient structure that can handle large volumes of data and complex queries.
- Data integrity and accessibility: Ensuring the integrity and accessibility of data is crucial. They must implement systems and protocols that maintain data accuracy and make it readily available for analysis.
- Alignment with business objectives: Data architects need to ensure that the data environment aligns with the business objectives. This means understanding the broader business strategy and ensuring that the data architecture supports these goals.
Qualifications and skills:
- Educational background: Typically holding a degree in Data Science, Computer Science, or a related field, Data Architects bring a deep understanding of data structures and database theory.
- Technical expertise: They should have a strong grasp of database design, data modeling, and SQL. Familiarity with cloud storage solutions and big data technologies is also essential, as these are increasingly becoming integral parts of modern data architectures.
- Strategic thinking: Beyond technical skills, they need to think strategically about data storage and management, ensuring that the architecture supports both current and future business needs.
Top tip: Choose candidates who are good at working with different teams and can turn business goals into technical plans, and explain technical details in business terms.
3. BI Developer
BI developers are the technical backbone of the BI team. They specialize in creating and setting up the tools and systems needed for effective data analysis and reporting. Their main job is to make sure these tools are strong and match the business’s specific requirements.
Responsibilities:
- BI tool development: Their primary focus is on developing effective BI tools. This involves not just coding but understanding how these tools can best serve the data analysis needs of the organization.
- Dashboard and report creation: They are responsible for creating dashboards and reports that are not only informative but also user-friendly, catering to the needs of various end-users within the organization.
- Maintenance and updates: Ongoing maintenance and updating of BI tools are key responsibilities. This ensures that the tools remain effective and relevant over time.
Qualifications and skills:
- Educational background: A typical BI Developer holds a Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science or a related field. This provides a strong foundation in the technical aspects of software and system development.
- Programming expertise: Proficiency in programming languages like Python or Java is essential. This skill set enables them to build and customize BI tools and applications.
- Experience with BI tools and systems: Hands-on experience with BI tools and database management systems is crucial. Familiarity with specific tools used within the organization or industry can be a significant advantage.
Top tip: Don’t underestimate the importance of Data Governance skills when hiring BI Developers. It ensures accurate, secure, and compliant BI solutions that align with the organization’s goals.
Staffing and scaling your BI team
The next important step is figuring out the best way to staff and adjust the size of your BI team.
In this section, we’ll look at how many people to hire for each role and knowing when to increase or decrease the team size based on the changing needs of your company.
How to decide on team size and who to hire
Besides knowing who to have on your BI team, it’s also useful to know how many people you need for each role.
Starting your team
- BI analysts: The range of skills required for effective BI is broad, including data visualization, report generation, and detailed data analysis. One person may not possess expertise in all these areas. Additionally, BI projects often involve handling large amounts of data and various tasks simultaneously.
For that reason, you should begin with 2-3 analysts for small to medium-sized projects. Each analyst can focus on a specific area, like data visualization or report generation. This way, you can make sure that all key aspects of business intelligence are addressed competently. Plus, their collaboration can lead to more effective solutions.
- Data architects: Typically, one data architect is sufficient. However, for projects involving complex data structures or large-scale data integration (like merging multiple databases or building a data warehouse from scratch), consider two architects for more efficient design and implementation.
This way, each architect can work on different parts of the data setup. For example, one can handle the technical side while the other makes sure it fits with the business’s plans.
- BI developers: Like BI analytics, BI development requires a wide range of skills, and it’s rare to find someone who’s an expert in everything. BI projects often include complicated tasks, such as managing data structures and creating tailored BI solutions.
So, when you’re building your BI team, think about getting a couple of BI developers, especially for smaller projects. This way, you can match each developer’s strengths to different parts of the project.
Having more than one developer also means they can work together to build BI tools for your business.
Adding specialized roles
As your business grows and your BI needs change, adding special roles to your team can really help.
Let’s look at the kinds of special roles that are good for bigger, more complicated projects:
- Data scientists: Data scientists are great for projects that need advanced analytics, such as predictive analytics, statistical analysis, and machine learning. They dig into complicated data to find useful information that helps in making big decisions.
If your project is really big or complex, you might need more than one data scientist.
- Data engineers: Data engineers are really important for building and maintaining robust data pipelines. Their primary role involves the technical aspects of data collection, ensuring that data is not only accurately gathered but also efficiently stored and made available for analysis.
Large-scale projects or those involving real-time data processing may require multiple data engineers.
- BI project managers: For larger projects or multiple concurrent initiatives, you’ll need a dedicated BI project manager.
BI project managers are key to managing BI projects effectively. They oversee the project lifecycle, coordinate between different BI roles, and ensure that project goals are met on time and within budget.
- BI managers: The business intelligence manager person leads the BI team, deciding on strategies and making sure they match the company’s goals. They are key in blending BI work with business operations.
In big companies or when BI work gets complicated, a BI manager is really important to keep everything organized and on track.
- Data governance manager: If your company handles sensitive data or needs to follow strict rules like GDPR or HIPAA, you’ll need a data governance manager. They make sure that the company has the right data policies and that everyone sticks to them. They take care of risks linked to keeping data safe and private.
Usually, one manager is enough to set up and look after these rules.
Need an external consultant for your business intelligence team?
If you need external consultants to enhance your BI team or project, feel free to reach out to us. We specialize in connecting you with top-notch external consultants who can bring valuable expertise to your organization.
Contact us today to explore how our external consultants can contribute to your business’s success.
When to scale up or scale down
Knowing when to change the size of your BI team is important to keep things efficient and match your organization’s evolving needs.
Here are some key indicators for when to scale up or scale down your team:
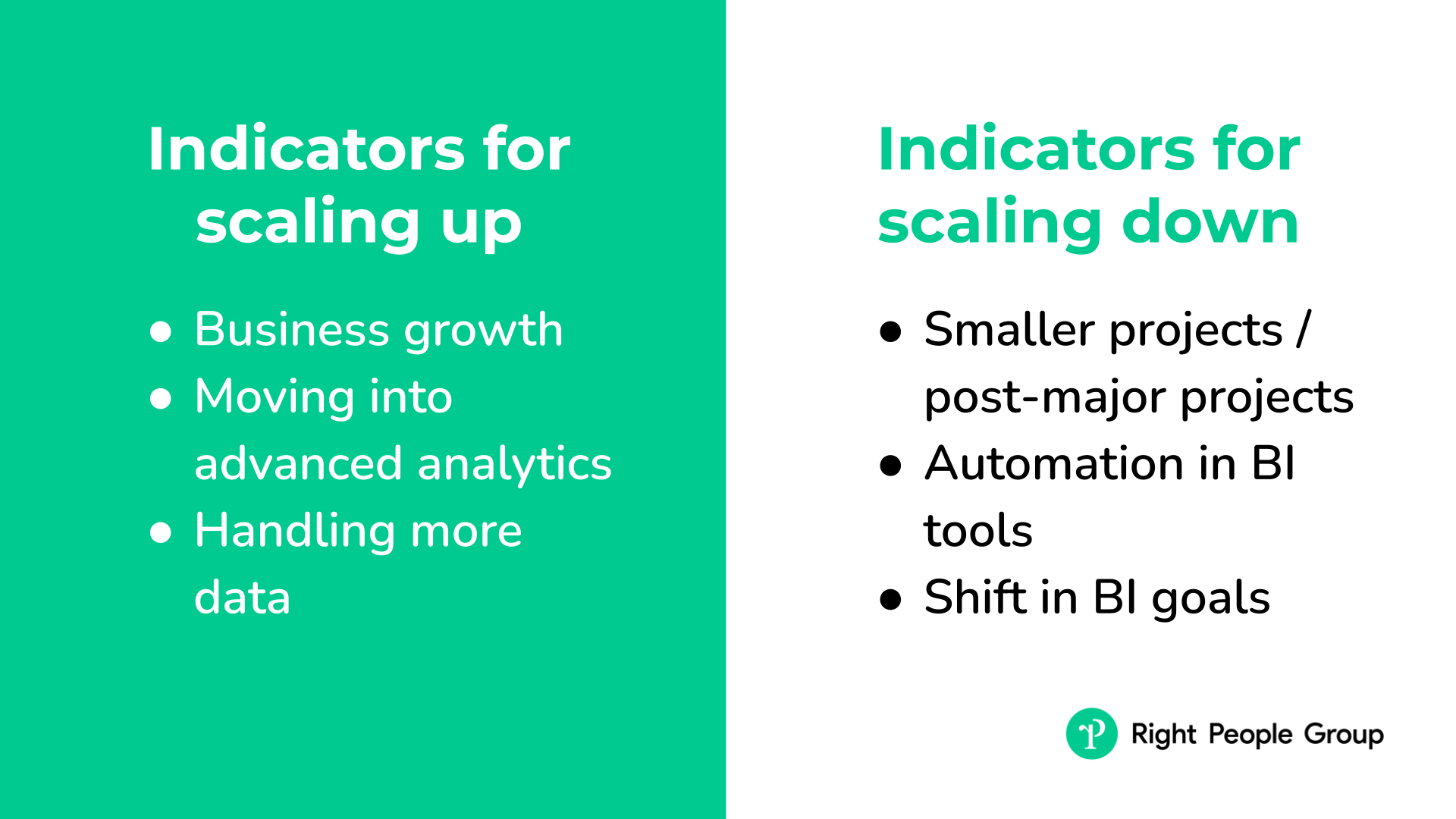
Indicators to scale up:
- Business growth and more data: Add to your team if your business is growing, or you’re dealing with more and different types of data and analytics.
- Moving into advanced analytics: Consider expanding your team for complex tasks like predictive modeling or real-time data analysis.
- Handling more data: Increase your team size if there’s a rise in the volume and variety of data that needs managing and analyzing.
Indicators to scale down:
- Smaller projects or post-major projects: You might need fewer team members if your BI projects are smaller in scope or after big projects wrap up.
- Automation in BI tools: If new BI tools are doing tasks automatically, some roles in your team might no longer be necessary.
- Shift in BI goals: Reduce your team size if your organization is shifting focus to certain BI goals, and less manpower is required.
Leverage BI consultants for flexibility
We have been linking businesses with highly skilled IT and business consultants, including Power BI consultants, since 2007. Our selection process ensures that we connect you with consultants who are not only knowledgeable in their field but also have a proven track record of successfully handling projects similar to yours.
Contact us, and we’ll help you find the ideal business intelligence consultant whose skills and experience are well-suited to your project’s specific needs.
Conclusion
Forming a Business Intelligence (BI) team is essential for businesses to make the most of their data. With careful preparation and a skilled BI team, companies can turn complex data into clear insights, leading to better decisions and growth in our data-focused world.