There used to be a time when companies had to deal with clunky servers stored in a basement.
Now, however, with cloud technology, businesses can get everything they need right through the internet. With cloud computing, employees have access to data, computing power, and even specialized software no matter where they are.
In this article, we’ll talk about the different cloud deployment models, the core service models available, and finally, the most popular platforms that businesses use and why.
Our goal is to give you a well-rounded understanding of the options available, including their features and uses.
Cloud deployment models
When choosing a cloud platform for your business, there are three main types of cloud deployment models to consider: public, private, and hybrid.
The type you choose depends on what works best for your business needs and goals.
Public cloud platforms
Public cloud platforms are provided by external companies and can be accessed online.
Google Workspace falls into this category as it offers a suite of cloud-based productivity and collaboration tools, such as Gmail, Google Docs, and Google Sheets, which can be accessed by businesses and individuals online.
Users can subscribe to Google Workspace services on a pay-as-you-go basis, making it a public cloud offering.
Key benefits and potential drawbacks
The key benefit for businesses is cost-effective scalability. This means that as a business grows and needs more computing power or resources, it can easily get them through these services without incurring high costs.
However, disadvantages include vendor lock-in, security and privacy, downtime planning, cost management, limited customization, data transfer costs, and compliance challenges. Careful evaluation of these factors is essential when considering cloud services.
Private cloud platforms
Private cloud platforms are operated exclusively for a single organization. These platforms provide enhanced control, security, and customization compared to public cloud offerings.
One example of a private cloud platform is VMware Cloud Foundation. It offers a dedicated and highly customizable cloud environment that businesses can use to run their applications and manage their data.
Organizations that opt for private cloud solutions typically do so to maintain strict control over their data and infrastructure. This approach ensures that sensitive information remains secure and in compliance with regulatory requirements.
Key benefits and considerations
The primary advantage of private cloud platforms is the level of control they offer. Businesses can customize the infrastructure to suit their precise performance and security requirements.
However, private cloud solutions require a higher upfront investment compared to public clouds. Companies must also handle their own maintenance, which can lead to additional operational costs.
Hybrid cloud platforms
Hybrid cloud platforms combine the features of both public and private clouds to offer versatile solutions.
IBM Cloud is an example of a hybrid cloud platform. It allows businesses to integrate their on-premises infrastructure with cloud resources, providing flexibility and scalability.
Users can customize their hybrid cloud setup to suit specific needs. For example, a company with stringent data security requirements can configure its hybrid cloud to keep sensitive information on a private cloud while using the public cloud for less sensitive operations, ensuring data integrity and regulatory compliance.
Key benefits and potential drawbacks
One major advantage is flexibility. Businesses can leverage their existing infrastructure while expanding into the cloud as needed.
However, considerations include complex management, potential integration challenges, data security, and compliance. Make sure you do a thorough evaluation before implementing a hybrid cloud model.
Further reading: How to leverage cloud consultants for your cloud migration project
Core service models
Once you’ve chosen a deployment model, it’s time to focus on the core service models that align with your business requirements.
These service models fall into 3 main categories, so let’s break them down.
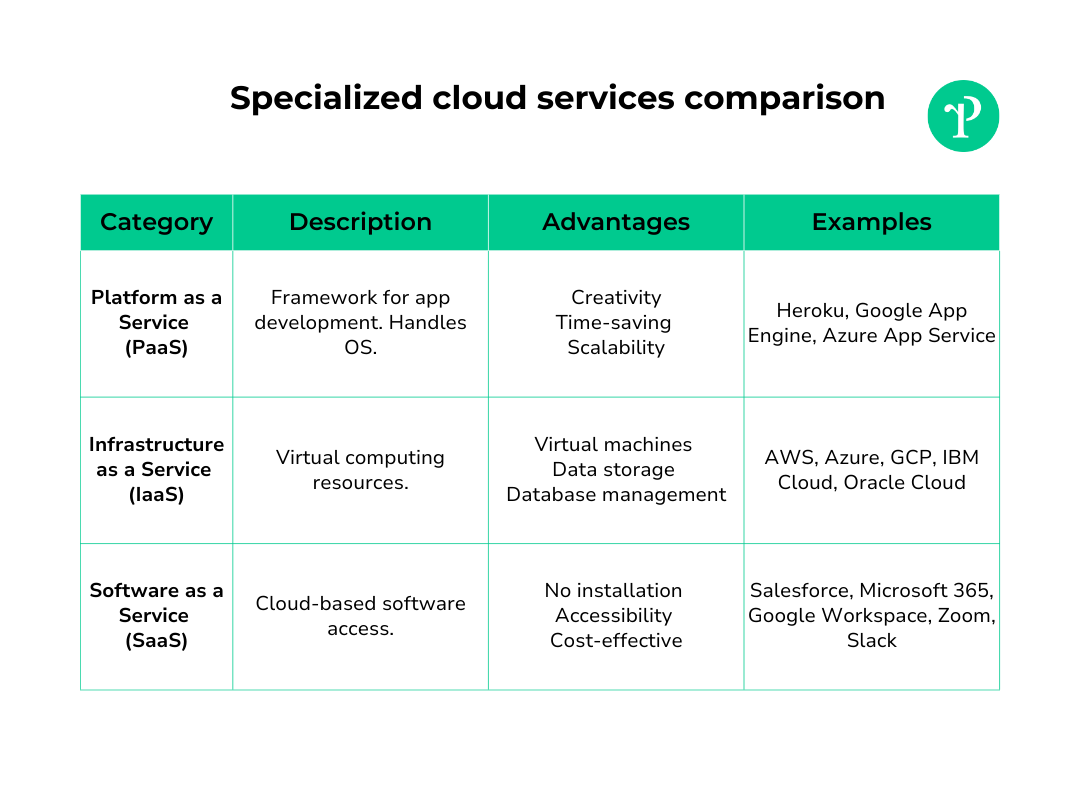
Platform as a service
PaaS providers offer a framework for developers to build upon. They handle the underlying operating system and allow users to focus on the application development.
Among its advantages are:
- Focus on creativity: Developers can channel their energy into creating amazing applications, not wrestling with operating systems.
- Saves time: PaaS takes care of the infrastructure, so you can roll out new software faster.
- Scalability: It’s easy to scale your applications as your business grows, thanks to the flexible nature of PaaS.
Some examples of Platform as a Service (PaaS):
- Heroku: A cloud platform that simplifies application deployment and management, ideal for developers.
- Google App Engine: Allows developers to build and deploy applications without managing infrastructure.
- Microsoft Azure App Service: A fully managed platform for building, deploying, and scaling web apps.
- Red Hat OpenShift: An open-source container platform for building, deploying, and managing applications.
- Salesforce Lightning: A platform for developing and deploying custom business applications.
Infrastructure as a service
IaaS is all about providing virtualized computing resources over the internet. This service can be used to run virtual machines, store data, or run databases.
Some of the advantages of IaaS include:
- Virtual machines: You can run virtual machines on IaaS, making it a breeze to set up and manage your computing resources.
- Data storage: Store your data securely in the cloud, without worrying about hardware failures.
- Database management: IaaS makes it easy to set up and manage databases, a vital part of many businesses.
Some examples of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Offers a wide range of infrastructure services, including virtual machines, storage, and networking.
- Microsoft Azure: Provides IaaS capabilities for building, deploying, and managing virtualized resources and applications.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Offers scalable infrastructure services, including virtual machines and storage, with a focus on data analytics.
- IBM Cloud Infrastructure: Provides IaaS solutions with a strong emphasis on security and hybrid cloud integration.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure: Offers high-performance IaaS for running enterprise workloads, databases, and applications.
Software as a service
SaaS offers the use of software over the cloud. Businesses can access software applications via the internet, eliminating the need to install and maintain software on individual computers. Here’s why businesses love it:
- No installation hassles: Say goodbye to the days of installing and maintaining software on individual computers. With SaaS, everything is in the cloud.
- Accessibility: Access your software from anywhere with an internet connection. It’s like having your office with you wherever you go.
- Cost-effective: SaaS often operates on a subscription model, so you pay for what you use without hefty upfront costs.
Some examples of Software as a Service (SaaS):
- Salesforce: A leading CRM platform offered as a SaaS solution.
- Microsoft 365 (formerly Office 365): Provides SaaS access to popular productivity software like Word, Excel, and Outlook.
- Google Workspace (formerly G Suite): Offers SaaS access to email, document collaboration, and other productivity tools.
- Zoom: A cloud-based video conferencing and communication tool.
- Slack: A team collaboration platform delivered as SaaS for real-time messaging and file sharing.
Major cloud platforms businesses use
Businesses are turning to cloud computing to improve their operations and here’s why:
- Scalability: Cloud services allow a business to easily adjust its digital resources based on needs. They can grow or scale back as required.
- Collaboration: A centralized cloud platform enables team members to work together efficiently. Regardless of their locations, they can access and share files.
- Integration: Cloud services integrate seamlessly with existing business systems, enhancing their efficiency.
If you’re looking for a reliable and feature-packed cloud service, there are a few big names that businesses trust the most:
Microsoft Azure
If you’re looking for a cloud service that plays well with Microsoft software, check out Azure. Loved by cloud professionals, it offers everything from SaaS to PaaS to IaaS (we explain what these are later in this article). It’s a fit for any business size and is built on a a well-designed and reliable cloud architecture.
Google Cloud Platform
If making smart, data-driven decisions is a priority for your business, Google Cloud should be on your shortlist. This popular cloud computing platform provides machine learning services and really shines when it comes to data analytics.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
If scalability and security are top priorities for your business, you might want to put AWS on your list. This cloud pioneer offers a wide array of computing resources and is especially known for its strong cloud security. It provides both public and private cloud options.
Oracle Cloud
If databases are the backbone of your business, take a look at Oracle Cloud. This cloud platform is all about database services and offers a secure, scalable environment to match.
Alibaba Cloud
If you’re doing business in Asia or looking to expand there, consider Alibaba Cloud. This cloud computing solution offers everything from data analytics to AI and machine learning, making it a top pick for companies operating in the region.
Salesforce
If you need to keep track of your customers and want to understand them better, Salesforce is worth a look. This well-known platform offers customer relationship management tools as a service and is a top pick for businesses focusing on customer data.
Oracle NetSuite
If managing your business’s finances, inventory, and operations all in one place is your aim, Oracle NetSuite is worth considering. This cloud-based ERP platform offers a unified environment to take care of those key business processes.
There are many other cloud computing platforms available, each with its own strengths and specializations. Research your options to find the cloud provider that best suits your goals.
Further reading: Building a successful cloud team: Structure, roles, and responsibilities
Conclusion
Cloud technology supports your ability to grow, work together effectively, and connect seamlessly. Being well-informed about these choices is crucial for improving efficiency, encouraging innovation, and reaching your business objectives.
As the cloud computing industry continues to evolve, you will have even more cloud computing services to choose from. We hope this guide is helpful for you in navigating the complex but rewarding world of cloud computing.